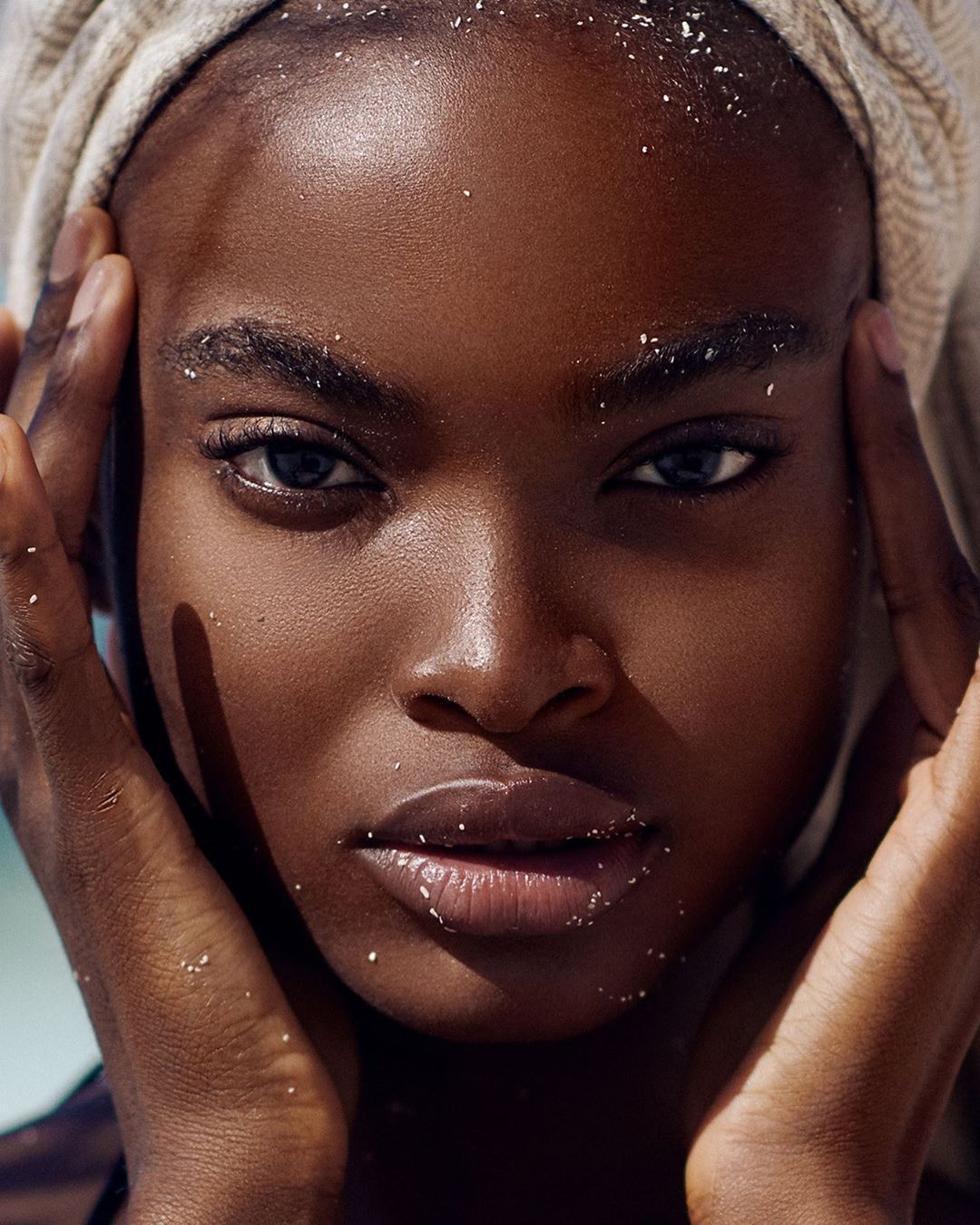
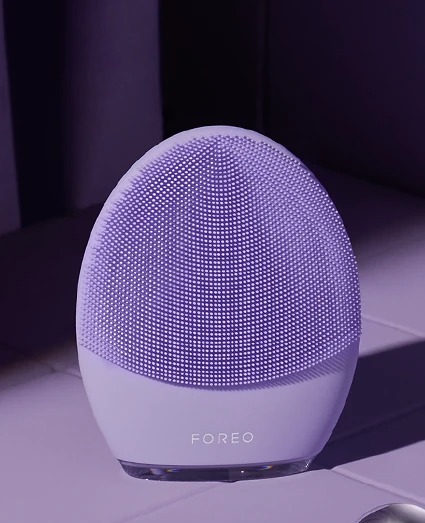
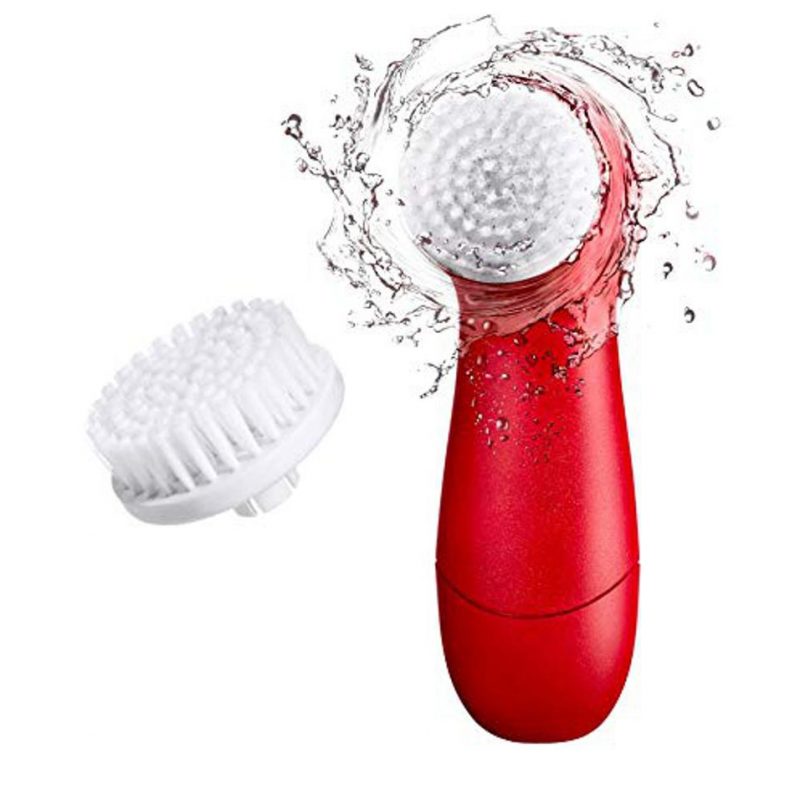
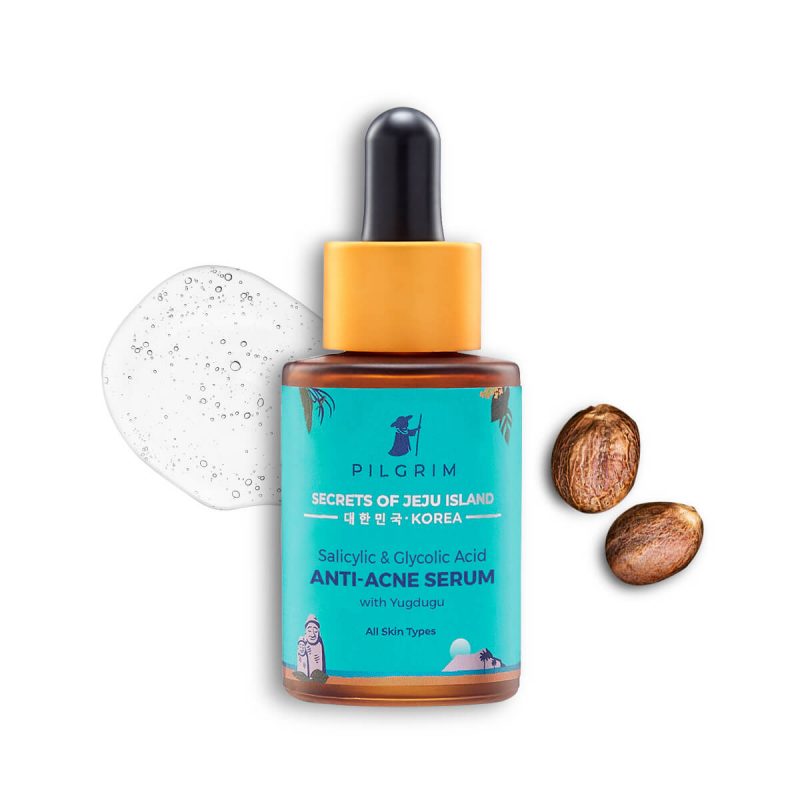
Many of you might not know it, but exfoliating is one of the most crucial steps in any skincare routine, as it helps remove dead skin cells and promote cell turnover, leaving the skin looking smoother and more radiant.
There are two main types of exfoliants: physical and chemical. Physical exfoliants, such as scrubs and brushes, work by physically sloughing off dead skin cells. On the other hand, chemical exfoliants use enzymes or acids to dissolve the bonds that hold dead skin cells together.
Some common physical exfoliants include:
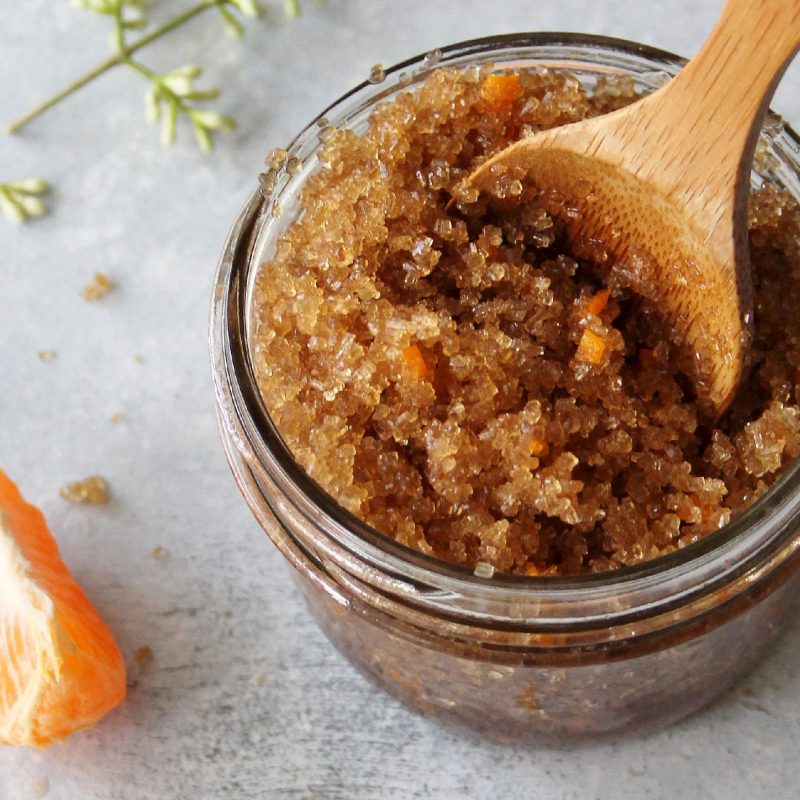
Sugar scrubs: These scrubs typically contain sugar mixed with a carrier oil, such as coconut or olive oil.
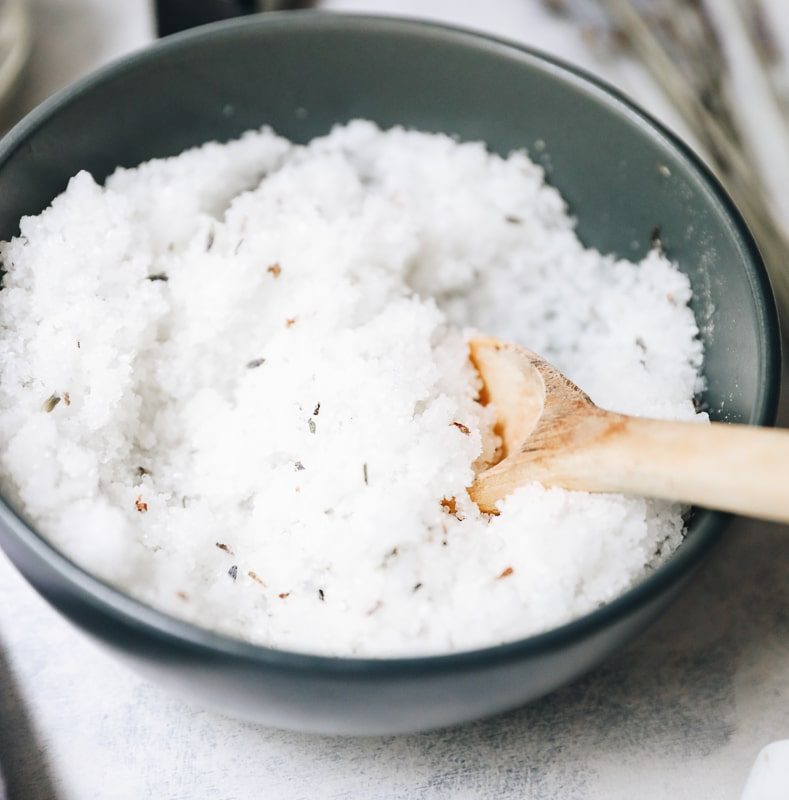
Salt scrubs: Similar to sugar scrubs, salt scrubs use salt as the exfoliating agent.
Facial brushes: These brushes are designed specifically for use on the face and come in various materials, including bristles, silicone, and rubber.
Some common Chemical exfoliants include:
Alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs): These acids, such as glycolic acid and lactic acid, work by dissolving the bonds between dead skin cells, allowing them to be easily washed away.
Beta-hydroxy acids (BHAs): These acids are oil-soluble and can penetrate deep into the pores to remove impurities and dead skin cells. A good example is the salicylic acid.
When exfoliating, it’s important to start with a gentle product and to use it sparingly. Over-exfoliation can lead to irritation, redness, and sensitivity. It’s also important to use sunscreen after exfoliating, as the process can leave the skin more susceptible to sun damage.
You must also pay attention to your skin type and customize your exfoliating routine accordingly. For example, if you have dry or sensitive skin, you may want to use a gentler exfoliant or exfoliate less frequently. If you have oily or acne-prone skin, you can use a stronger exfoliant or exfoliate more regularly.